Blog Posts Tagged Technical Content
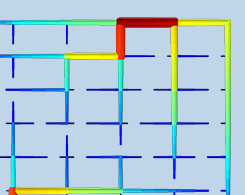
Designing District Heating Networks Using Topology Optimization
District heating networks help power plants reach high efficiencies by utilizing cogeneration, which is especially helpful in the winter. How does topology optimization fit in? Keep reading…
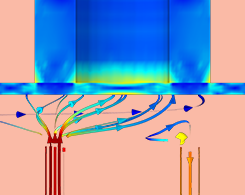
How to Simulate a Piezoelectric Micropump
Learn how to combine piezoelectric materials with fluid-structure interaction effects, use a velocity-dependent formula, and set up disconnected mesh between the solid and fluid domains.
Simulating a Silicon Quantum Dot in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Solar cells, LEDs, displays, photodetectors, and quantum computing are all potential applications of quantum dots, an essential aspect in the field of nanotechnology.
Using Global Equations to Introduce Fully Coupled Goal Seeking
Learn how to introduce a goal-seeking equation, combined with a fully coupled approach, to solve a nonlinear model. (Follow-up to an earlier blog post on goal seeking with a segregated solver.)
Introducing Goal Seeking into the Segregated Solver
Did you know that you can adjust a model input to achieve a desired output in your nonlinear problems? The process involves implementing a global equation into the segregated solver.
Modeling Acoustical Properties of Porous Media in COMSOL®
A guest blogger from the University of Sheffield introduces the Johnson–Champoux–Allard–Lafarge (JCAL) model for analyzing acoustical properties of porous media.
How to Analyze Turbomolecular Pumps with COMSOL Multiphysics®
Modeling gas flow in a turbomolecular pump calls for specialized numerical methods, because at such low pressures, the gas molecules rarely collide with each other.
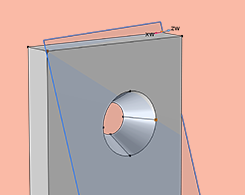
Modeling Parts Without Constraints in Your Structural Analyses
When building a solid mechanics model, there may be parts with prescribed loads but no constraints that can be reasonably applied. Learn different approaches and considerations for this scenario.
