Electromagnetics Blog Posts

A Multidisciplinary Approach to Electronics Design
Sharp is a powerhouse in the electronics industry, involved in televisions, liquid crystal displays, LED lighting systems, solar cells, multi-function business machines, and many other electronics-based products. One of a global network of Sharp R&D laboratories, Sharp Laboratories of Europe (located in Oxford, England), has been busy researching and developing LED lighting, display technology, microfluidic lab-on-a-chip, and energy systems for incorporation into Sharp’s products.

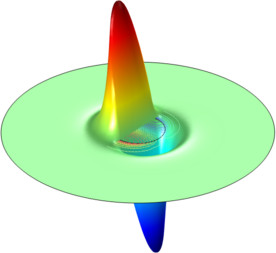
Quick Intro to Permanent Magnet Modeling
I’ve written several blog entries involving permanent magnets, in one way or another. Reading those may have raised the question “what about a more simple introduction to permanent magnet simulations?” Fair enough, here’s how to model a permanent magnet and its surrounding magnetic field.
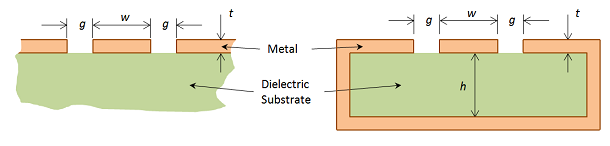
Modeling of Coplanar Waveguides
The Coplanar Waveguide (CPW) is commonly used in microwave circuits. COMSOL Multiphysics, with the RF Module, makes it easy to compute the impedance, fields, losses, and other operating parameters needed when designing a CPW.

A Recipe for Induction Stove Design Using Multiphysics Simulation
When I was little, I used to love spending the night at my grandparents’ house, where I was allowed to watch TV, stay up late, and in the morning, help my grandmother make pancakes. The hardest part was always waiting for her old, slow electric burner to heat up — to my six-year-old self, it seemed to take hours for the burner to become hot enough after we’d finished mixing the batter. Luckily for me, and for other impatient chefs […]

The Graphene Revolution: Part 5
In a paper titled “Choosing a Gate Dielectric for Graphene Based Transistors“, the applications of a semiconducting form of graphene are examined. As we have seen before, single-layer graphene is not a semiconductor, it is a zero bandgap conductor (a semimetal). Efforts are well underway to introduce bandgaps to graphene, which would make it semiconducting with a room temperature mobility an order of magnitude higher than silicon. The race is already underway to find applications for such a material once […]
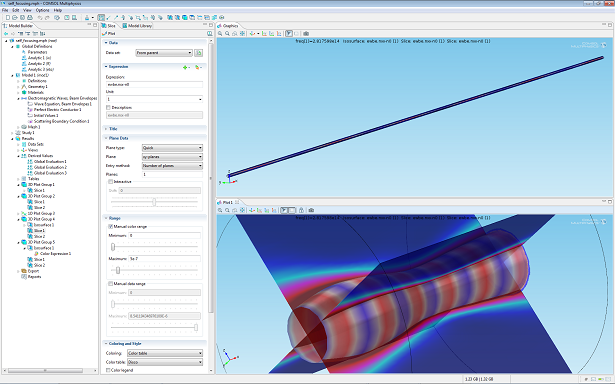
Taking Care of Fast Oscillations with the Wave Optics Module
The new COMSOL Multiphysics Wave Optics Module provides engineers with a great set of features for designing their simulations. One of the new capabilities included in this module is the groundbreaking beam envelope method for electromagnetic full-wave propagation. We hope this feature will become instrumental to the optics community.
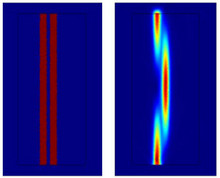
Wave Optics, to Approximate or Not?
Engineers working with lasers, optical fibers and waveguides, nonlinear optical processes, metamaterials, and other large photonic devices ultimately deal with wave optics. Photonic devices are considered “large” when they are larger than a wavelength of light. In that case, you deal with optics frequencies as opposed to radio frequencies, and the device is not complex enough to justify approximating with rays.
Step-Index Fiber Simulation
Optical fibers are used to transmit information in the form of light through an optical waveguide made of glass fibers. The light is sent in a series of pulses that can be translated as binary code, allowing the transfer of information through the fiber. Because such pulses can travel with less attenuation and are immune to electromagnetic disturbances, fibers are used instead of traditional metallic wires thus allowing data transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths.
