Latest Posts
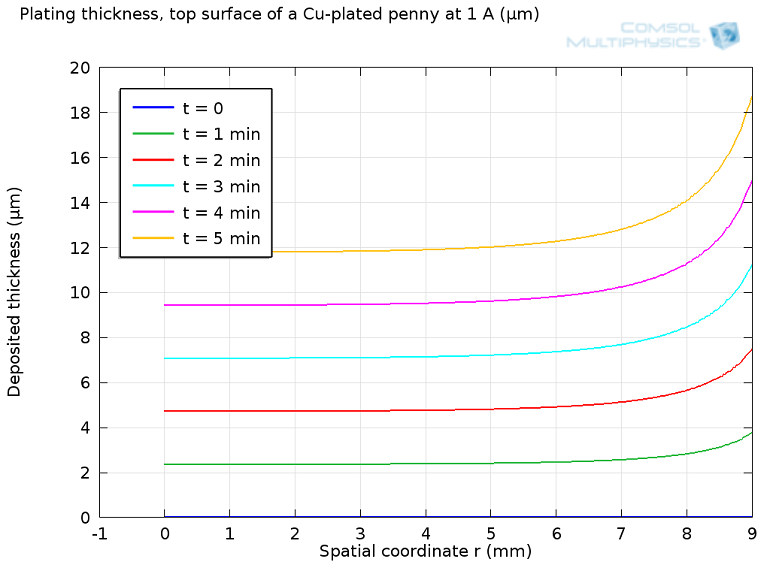
Electroplating: How the U.S. Mint Makes a Penny
Did you know that a penny actually doesn’t contain a lot of copper? Learn about how the U.S. Mint makes pennies through the process of electroplating, which can be studied with chemical modeling.
Geometric Kernels in COMSOL Multiphysics®
Do you know what a geometric kernel is? This software component is responsible for handling geometry in COMSOL Multiphysics®. Get a comprehensive background of what this means…

Where Can I Find COMSOL Multiphysics Tutorial Models?
There are 2 ways you can find COMSOL’s tutorial models: The online Application Gallery includes downloadable resources and the Application Library makes models available directly in the software.

What Kinds of FSI Problems Can COMSOL Multiphysics Solve?
We discuss the various techniques for modeling fluid–structure interaction (FSI) in the COMSOL® software, as well as highlight the add-on modules you need for these various types of analyses.

Building a Beowulf Cluster for Faster Multiphysics Simulations
In 1994, NASA researchers built a small cluster of normal workstations. They called this parallel workstation Beowulf. Today, “Beowulf cluster” describes clusters built from normal workstations.
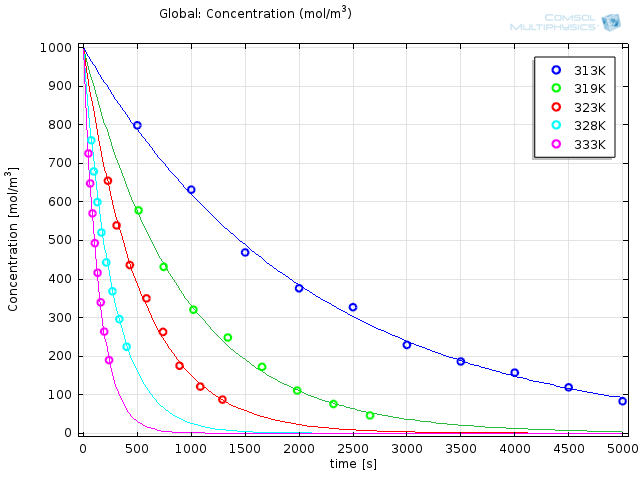
Chemical Parameter Estimation Using COMSOL Multiphysics
In this installment of our blog series on chemical kinetics, we discuss how to estimate the chemical parameters of your model in COMSOL Multiphysics®.

Modeling the Hydrostatic Pressure of a Fluid in a Deformable Container
Picture a water balloon being compressed at the center. As you squeeze the balloon, the locations of the highest point and depth of fluid change, altering the hydrostatic pressure distribution.
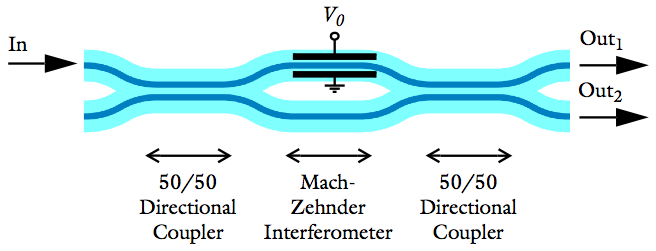
Optimizing Mach-Zehnder Modulator Designs with COMSOL Software
3 design requirements for a Mach–Zehnder modulator: It must produce low loss, give a 50/50 split of power through the 2 output arms, and be used as a spatial switch. See how simulation can help.



