Latest Posts

Automate Your Modeling Tasks with the COMSOL API for use with Java®
You can automate your coffee-making process, so why shouldn’t you be able to automate your modeling tasks? You can, using the COMSOL API for use with Java®.
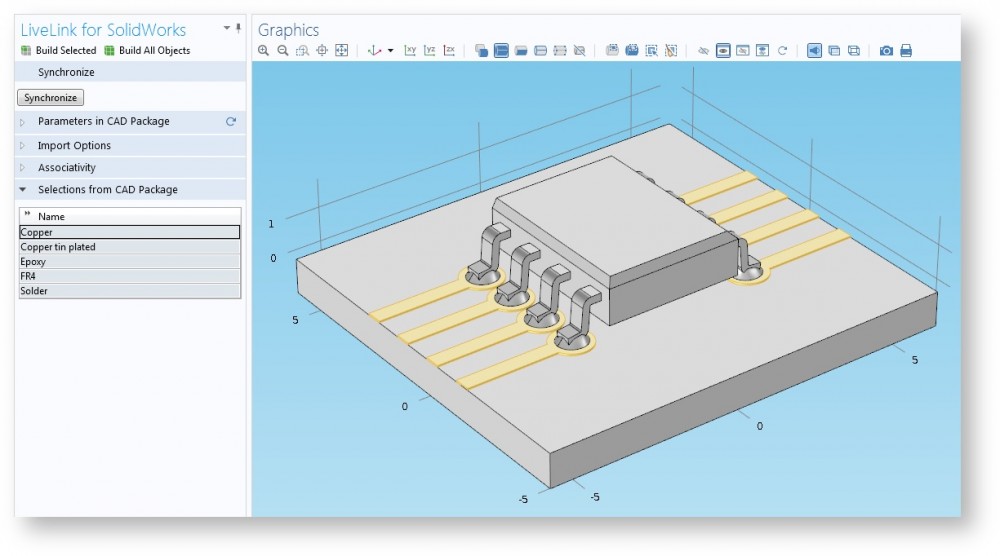
Synchronizing Selections Between SolidWorks® and COMSOL Multiphysics®
Learn how to synchronize selections between SOLIDWORKS® and COMSOL Multiphysics® via LiveLink™ for SOLIDWORKS® (as well as why you should!)
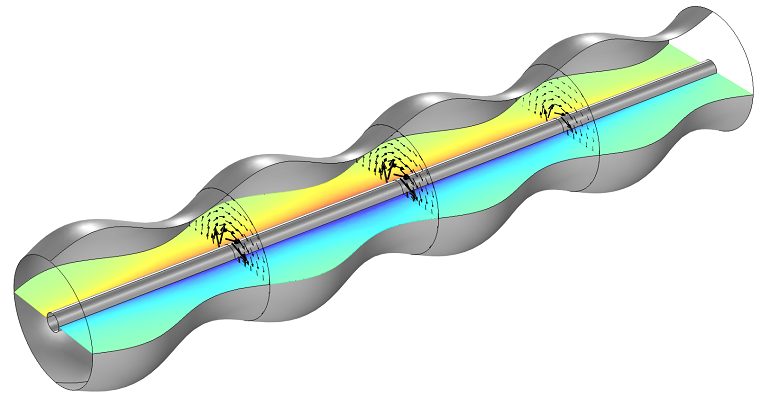
Computing the Impedance of a Corrugated Waveguide
Did you know that you can compute the effective impedance for waveguides with nonuniform cross sections (such as corrugated waveguides) in COMSOL Multiphysics®? We demonstrate how here >>

Happy Birthday, Josef Stefan
Josef Stefan is known for deriving the relationship between the radiant energy of a blackbody and its temperature, known as the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Learn more about the Austrian physicist.
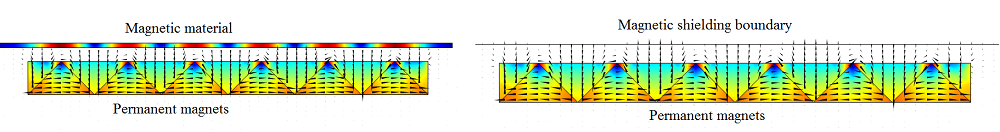
Calculate the Force of a One-Sided Magnet
Magnets: How do they work? You can calculate the force of a one-sided magnet using COMSOL Multiphysics® and the add-on AC/DC Module.

Added Value of Task Parallelism in Batch Sweeps
You can use batch sweeps to improve your modeling performance when you reach limitations in parallel computing. Learn how in this part of our Hybrid Modeling blog series.
Simulating Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability and Climate Dynamics
Q: What do heated soap bubbles, wavy clouds, and Jupiter’s Great Red Spot have in common? A. An unstable motion called Kelvin-Helmholtz instability.
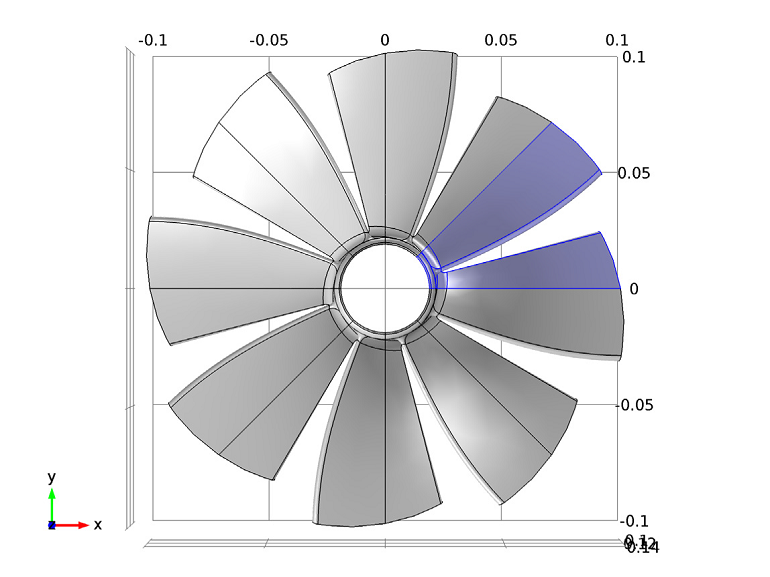
Using Cyclic Symmetry to Reduce Computation Time
Cyclic symmetry can be more complex for rotationally geometries than it can for axially symmetric geometries. Learn how to implement this feature to cut down on computational memory.
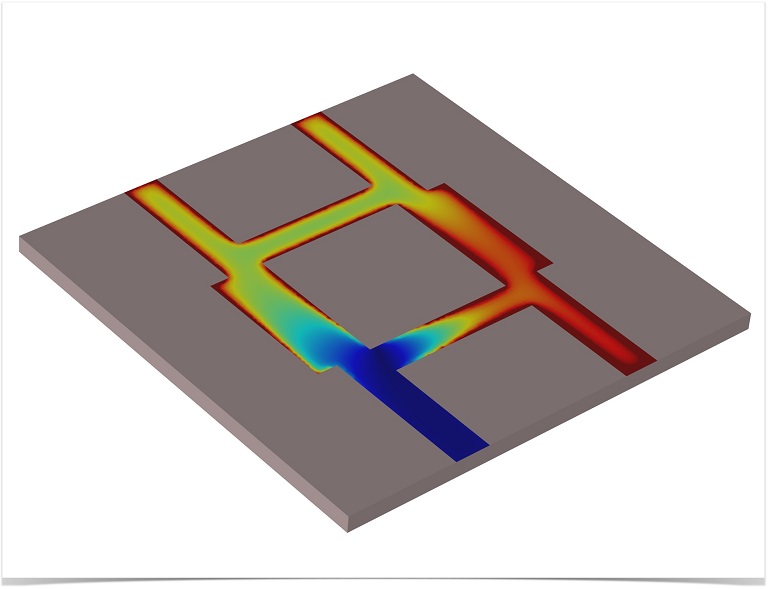
Modeling a Branch Line Coupler
A branch line coupler is made up of 2 sets of coupled ports with a phase difference of 90° between them. Power enters through 1 input port and is then divided equally between 2 output ports.
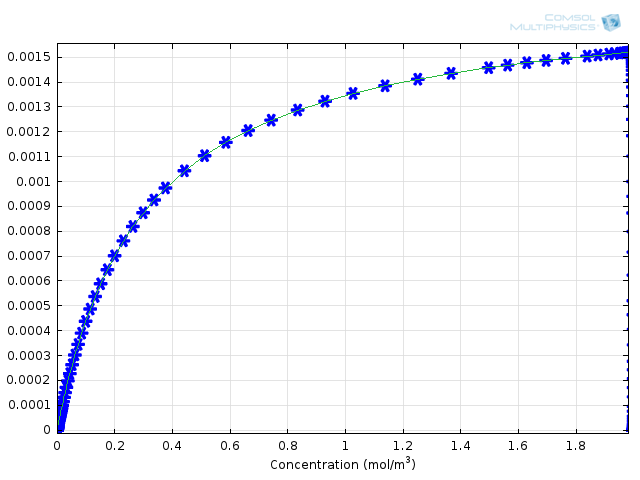
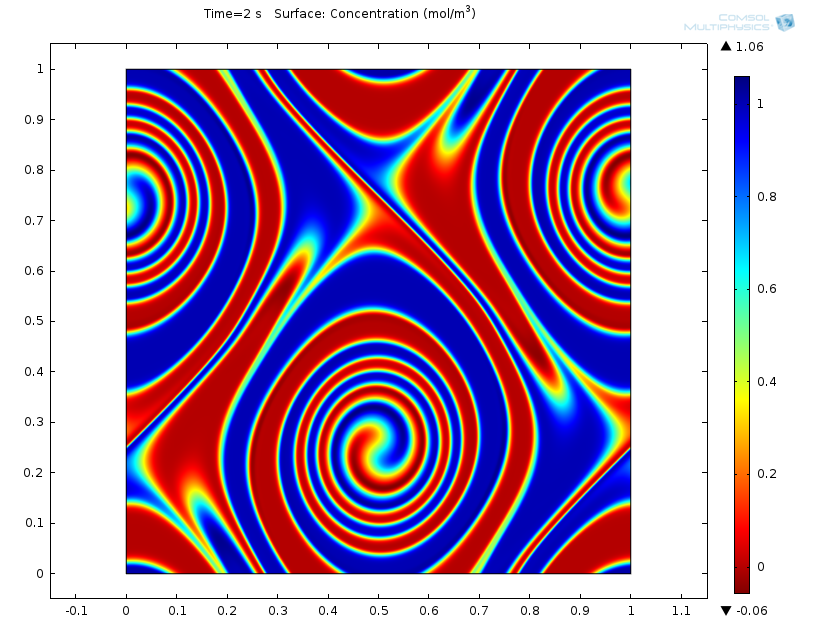
Enzyme Kinetics, Michaelis-Menten Mechanism
For the 100-year anniversary of the Michaelis–Menten mechanism, we honor the trailblazing publication the best way we know how — with simulation.
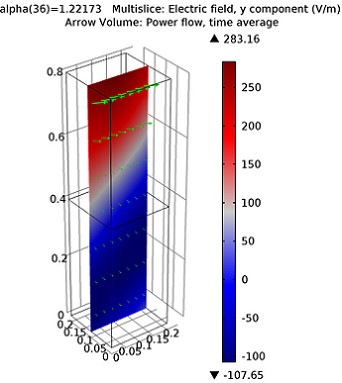
Benchmark Model Results Agree with Fresnel Equations
Bright idea: When a ray of light (an electromagnetic wave) propagating through free space hits a dielectric medium, part of the light will be transmitted and part will be reflected.

Defining Curvilinear Coordinates for Anisotropic Materials
Consider a carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer with woven fibers embedded in an epoxy matrix. How can you express the anisotropy by referring to the well-known Cartesian coordinate system?
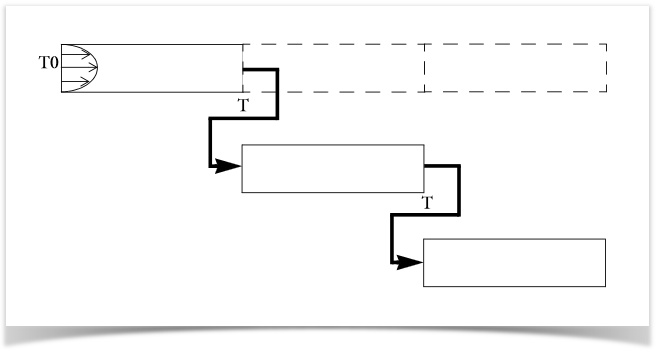
Solutions as Starting Point Values with LiveLink™ for MATLAB®
Did you know that if you want to map data from 1 COMSOL Multiphysics® solution to the next using MATLAB® scripting, you can do so by connecting the 2 software programs via LiveLink™ for MATLAB®?
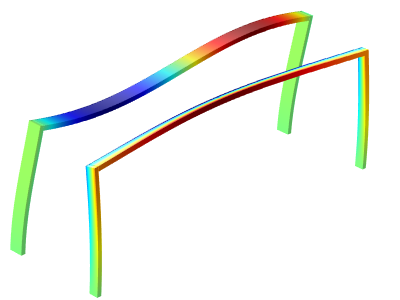
Buckling, When Structures Suddenly Collapse
The easiest way to approach a buckling problem — like a bridge collapse or crushed soda can — is by performing a linearized buckling analysis. See how to do so in COMSOL Multiphysics® here >>

Hybrid Computing: Advantages of Shared and Distributed Memory Combined
Shared memory platform + distributed memory platform = hybrid computing. Learn about the various aspects of hybrid computing and modeling in this installment of our blog series.
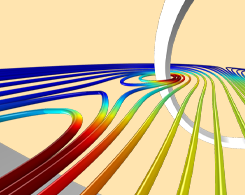
Plotting Spatial Derivatives of the Magnetic Field
Radiology, magnetophoresis, particle accelerators, and geophysics are all areas where it is useful to compute the spatial derivative of the magnetic field or magnetic flux density.
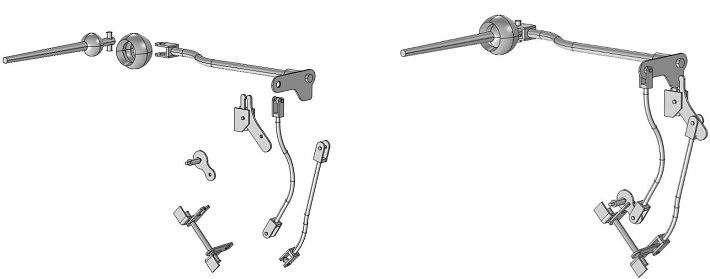
Selecting First Gear: Investigating a Classic Car Gearshift Mechanism
Follow along as we perform a multibody dynamics analysis of the gearshift mechanism in a classic car. Read to hit the road?
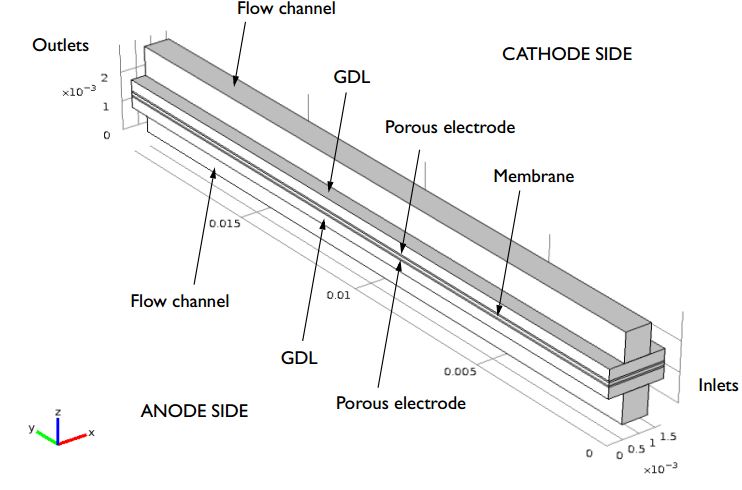
PEM Fuel Cell Modeling Examples
What can you study in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell? Mass transport, ohmic losses, temperature distribution, species transport, serpentine flow…should we keep going?
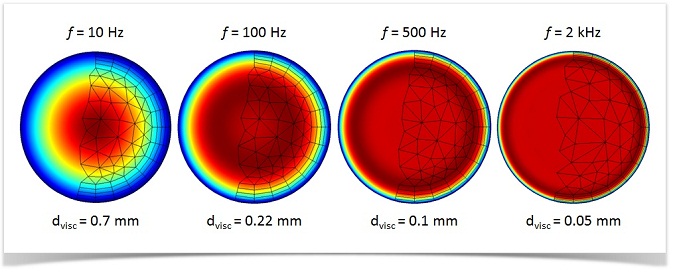
How to Model Thermoviscous Acoustics in COMSOL Multiphysics
Want to solve your acoustics model for acoustic pressure, velocity, or temperature variation? Enter the Thermoviscous Acoustics interface, which offers a simple and accurate way.
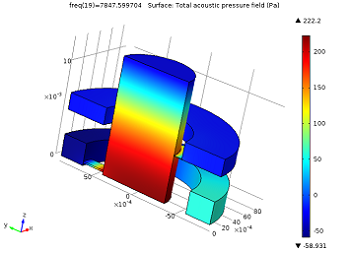
Theory of Thermoviscous Acoustics: Thermal and Viscous Losses
Here’s your comprehensive introduction to thermoviscous acoustics. Topics covered include theory, physics, boundary layers, bulk losses, attenuation, and narrow region acoustics.
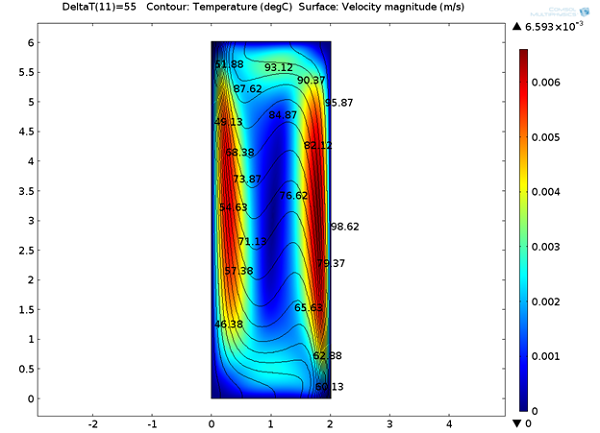
Buoyancy-Driven μPCR for DNA Amplification
True crime + simulation: The more DNA in a sample, the easier it is to accurately test and identify biomolecules, cells, and even an entire person during forensic investigations.

World’s Largest Solar Power Plant
Have you ever made the drive from Los Angeles to Las Vegas through the Mojave Desert? If so, you might have seen the world’s largest solar-based thermal power plant.

Intro to the What, Why, and How of Distributed Memory Computing
In a follow-up to our post on shared memory computing, we discuss another building block of hybrid parallel computing: distributed memory computing.

Happy Birthday, Nicolaus Copernicus
Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus first theorized the concept of a heliocentric universe. At the time, this was controversial. Now, more than 500 years later, we believe him.
