Negative Surface Discharge at Gas–Solid Interface
Application ID: 129251
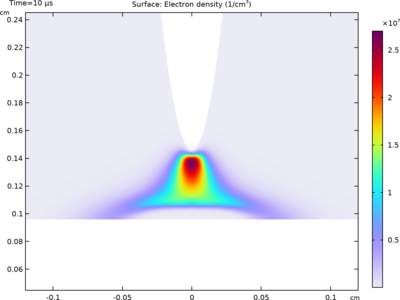
This model simulates a negative dielectric barrier discharge under a point-to-plate electrode configuration. Two solid dielectric layers are inserted into the air gap. A negative voltage of 2.5 kV is applied to the cathode electrode, initiating a corona streamer that propagates and generates a current pulse. The resulting negative charge carriers accumulate at the gas–solid interface, altering the electric field. Ultimately, a stable negative surface discharge is formed. The simulated discharge current and surface charge distribution at the gas–solid interface show excellent agreement with experimental results.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
