Ohmic and Activation Losses in a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Water Electrolyzer Cell
Application ID: 139561
In a polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzer cell, hydrogen and oxygen gas is produced by electrolysis. The hydrogen and oxygen compartments are separated by a polymer membrane, that also acts as electrolyte.
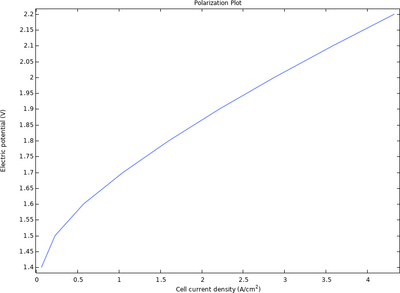
This introductory tutorial computes the ohmic and activation losses in a membrane-electrode assembly (MEA) in a polymer-electrolyte membrane water electrolyzer. The model geometry is in 1D and comprises two porous transport layers (PTLs) and one membrane domain.
The exterior boundaries of the hydrogen and oxygen PTLs are assumed to be at equilibrium with fully humidified gas streams, and gas diffusion is assumed to be fast, hence no mass transport or momentum transfer is included in the model
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
