Viscous Damping of a Microperforated Plate in the Slip-Flow Regime
Application ID: 113521
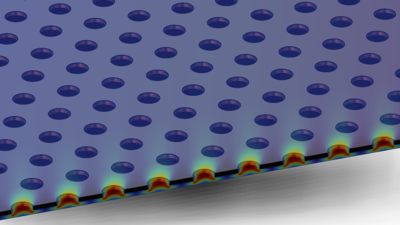
This tutorial model is of a micro perforated plate (also known as MPP) backed by a vibrating structure. This is a typical configuration in, for example, a MEMS microphone. The vibrating structure is not modeled explicitly, but just assigned a vibration velocity. The vibrating structure creates a pressure field that squeezes air through the perforated membrane. In the system there are two main sources for viscous losses: viscous losses in the squeezing flow between the gap between the vibrating structure and perforated membrane, and the viscous losses from the flow through the holes in the perforates. In this model the optimal hole size, to achieve minimal resistive losses, is analyzed for a given gap height and a fixed porosity (area ratio) for the perforates. The results are compared to the analytical results by Homentcovschi and Miles.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
